Monthly Scientific Update – February 2023
LCK Inhibitor: A Novel Potential Therapy for Cholangiocarcinoma
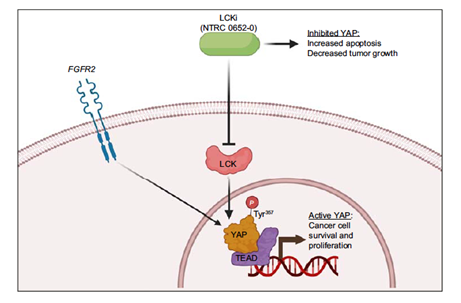
A variety of signaling pathways can become overactive in cancer to promote cell growth. One of these pathways is known as the Hippo signaling pathway, which involves the activation of “yes-associated protein” (YAP).
YAP is regulated by another protein called LCK, which can turn on YAP through reversible chemical modification (tyrosine phosphorylation). A recent study thus tested whether novel LCK inhibitors could decrease YAP activity and thereby slow cholangiocarcinoma growth.
To begin, the researchers developed a small molecule inhibitor (NTRC 0652-0) targeting LCK. NTRC 0652-0 exhibited high binding specificity for LCK, and treatment with the novel inhibitor decreased tyrosine phosphorylation in a pattern comparable to knocking out the LCK gene (Figure 1). These results confirmed that NTRC 0652-0 is a specific and effective LCK inhibitor, so the researchers proceeded to test its impact on YAP activity and cholangiocarcinoma growth.
In lab-based cholangiocarcinoma cell models, treatment with NTRC 0652-0 caused decreased YAP tyrosine phosphorylation-an indication of diminished YAP activity. Accordingly, NTRC 0652-0-treated cells showed increased cancer cell death.
A subset of patient-derived cholangiocarcinoma organoids with FGFR2 gene fusions were also sensitive to LCK inhibition by NTRC 0652-0. Progressing from cell culture to animal models, the study also demonstrated that oral treatment with NTRC 0652-0 slowed tumor growth in FGFR2 fusion-positive mouse models.
Although early stage, these results are promising and merit further investigation in additional animal and potentially human trials. Additional treatments for cholangiocarcinoma are urgently needed, and LCK inhibition is a promising strategy that could create new treatment options for many cholangiocarcinoma patients.
Reference:
Conboy CB, Yonkus JA, Buckarma EH, Mun DG, Werneburg NW, Watkins RD, Alva-Ruiz R, Tomlinson JL, Guo Y, Wang J, O’Brien D, McCabe CE, Jessen E, Graham RP, Buijsman RC, Vu D, de Man J, Ilyas SI, Truty MJ, Borad M, Pandey A, Gores GJ, Smoot RL. LCK inhibition downregulates YAP activity and is therapeutic in patient-derived models of cholangiocarcinoma. J Hepatol. 2023 Jan;78(1):142-152. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.09.014. Epub 2022 Sep 24. PMID: 36162702. 

Kelly Butler is an NIH Postbac Research Fellow and the Founding Director of SAFE